
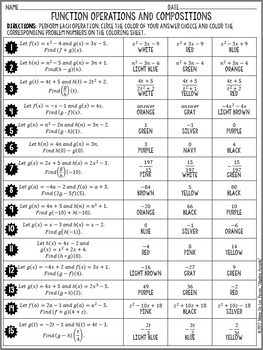
To perform the composition of functions you only need to perform the following steps: Select the function composition operation you want to perform, being able to choose between (fg) (x) and (gf) (x).

The composition operator ( ○) indicates that we should substitute one function into another.If a horizontal line intersects a graph more than once, then it does not represent a one-to-one function. is used to determine whether or not a graph represents a one-to-one function. The horizontal line test If a horizontal line intersects the graph of a function more than once, then it is not one-to-one. are functions where each value in the range corresponds to exactly one element in the domain. The composition calculator obtains the composite functions by following steps: Input: Enter the values of both f(x) and g(x) functions in specified fields. One-to-one functions Functions where each value in the range corresponds to exactly one value in the domain. Functions can be further classified using an inverse relationship. We use the vertical line test to determine if a graph represents a function or not. /rebates/2fhotmath2fhotmathhelp2ftopics2foperations-on-functions&. Recall that a function is a relation where each element in the domain corresponds to exactly one element in the range. ( f − 1 ○ f ) ( x ) = f − 1 ( f ( x ) ) = f − 1 ( 1 x − 2 ) = 1 ( 1 x − 2 ) + 2 = 1 1 x = x ✓Īnswer: Since ( f ○ f − 1 ) ( x ) = ( f − 1 ○ f ) ( x ) = x they are inverses. To perform the composition of functions you only need to perform the following steps: Select the function composition operation you want to perform, being able to choose between (fg)(x) and (gf)(x). Draw an arrow diagram for a function \(f: A \to B\) that is a bijection and an arrow diagram for a function \(g: B \to A\) that is a bijection.( f ○ f − 1 ) ( x ) = f ( f − 1 ( x ) ) = f ( 1 x + 2 ) = 1 ( 1 x + 2 ) − 2 = x + 2 1 − 2 = x + 2 − 2 = x ✓.
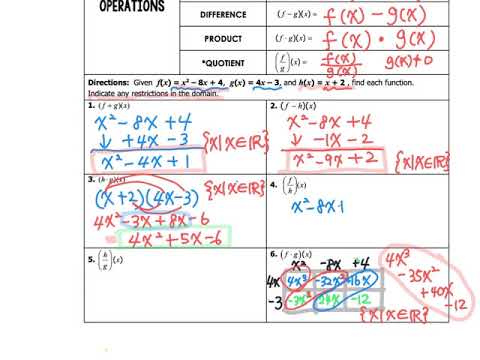
In this case, is the composite function \(g \circ f: A \to D\) a surjection? Explain. Draw an arrow diagram for a function \(f: A \to B\) that is a surjection and an arrow diagram for a function \(g: B \to D\) that is a surjection.one in that I not only have to do the operations with the functions. When vertical bars are used to denote absolute value, this calculator is not designed to handle the case of absolute value expression nested inside another absolute value expression because its too ambiguous to interpret users intention. The addition, multiplication, subtraction, division and composition of functions are all. For each absolute value expression, make sure that a matching pair of vertical bars are used.
#Operations and compositions of functions calculator free#
In this case, is the composite function \(g \circ f: A \to C\) an injection? Explain. Free functions composition calculator - solve functions compositions step-by-step. A graphing calculator to explore the operations on functions. Draw an arrow diagram for a function \(f: A \to B\) that is an injection and an arrow diagram for a function \(g: B \to C\) that is an injection.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
